仓库
仓库
本文将讲解git一些基础操作,所有内容都是围绕着本地仓库进行讲解的,比如提交修改,撤销修改,查看仓库状态,查看历史提交等基本操作,学习完这些操作,基本上就可以上手使用git了。
创建仓库
git的所有操作都是围绕着git仓库进行的,一个仓库就是一个文件夹,它可以包含一个项目代码,也可以包含很多个项目代码,或者其他奇奇怪怪的东西,到底要如何使用取决于你自己。创建仓库首先要创建一个文件夹,执行命令创建一个example文件夹。
$ mkdir example
进入该文件夹,执行git初始化命令git init,就可以为当前文件夹创建一个git仓库
$ cd example
$ git init
命令初始化完毕后,当前文件夹下就会多出一个名为.git的文件夹,里面存放着当前仓库所有的信息。
$ ls -a
./ ../ .git/
到此就创建好了一个基本的git仓库。
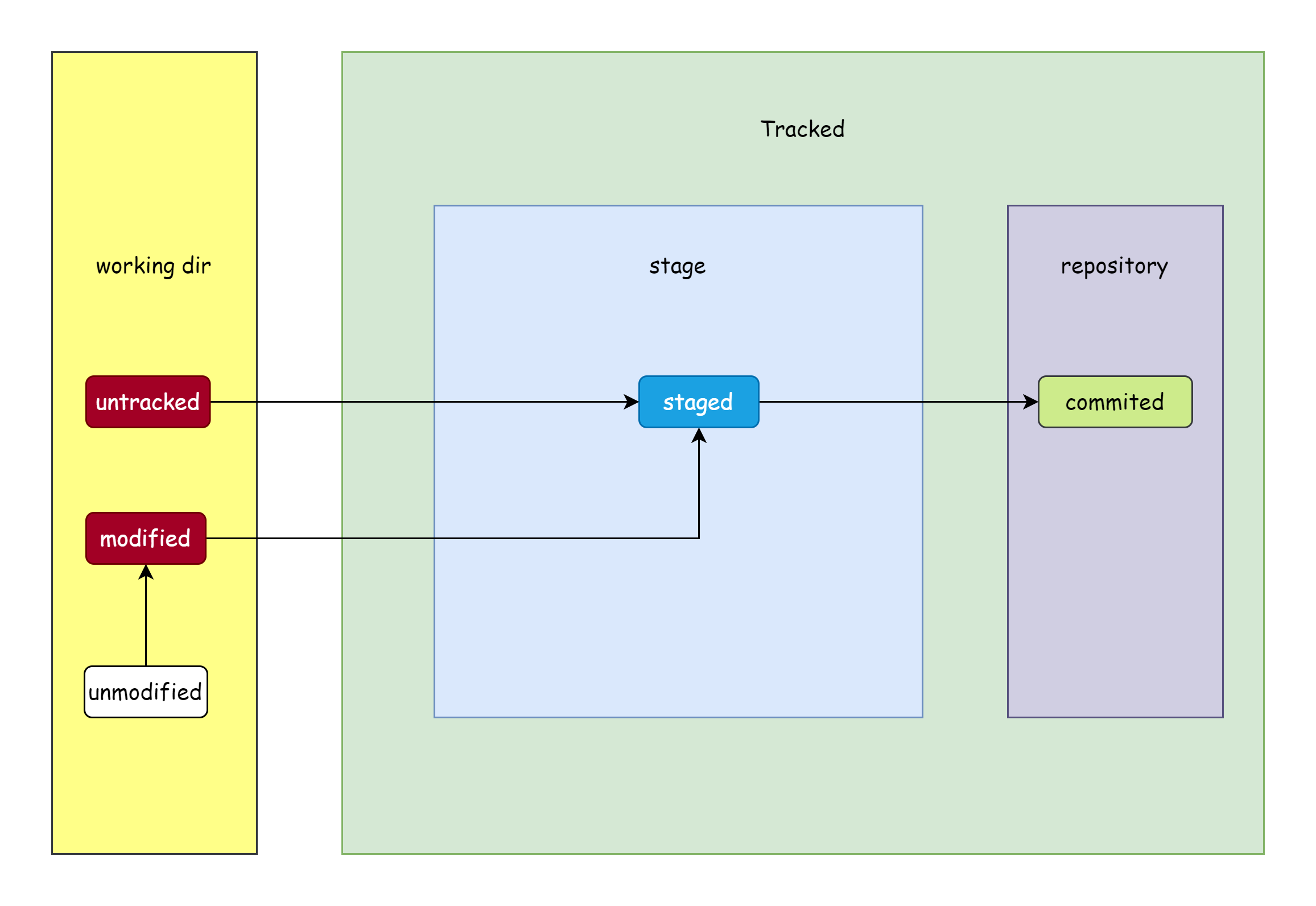
介绍一些基本的概念,首先要明白的是,在已创建的example目录内,除了.git文件夹,其他的所有文件或文件夹都属于工作区(图中黄色部分),日后所有对文件的修改,新增,删除的操作都是在工作区进行。操作过后,我们必须要手动指定git追踪哪些文件,这样git才能将指定文件纳入版本控制当中,这一步就是追踪文件,将其添加到暂存区(图中蓝色部分),然后就将这些修改提交到仓库(图中的紫色部分)后,才算是真正的由git仓库记录了这一次修改。除此之外,还有一个将本地仓库的修改推送到远程仓库的步骤,不过这是可选的。
暂存修改
当前仓库什么都没有,所以接下来要创建几个文件来进行管理。
$echo "hello git, this is my 1st repo!" > hello.txt
$ echo "#Hi there" > README.md
在上面的命令中,创建了一个hello.txt文本文件,还有一个名为README.md的markdown文件。名为README的文件往往具有特殊意义,它的名字就是read me,即阅读我,该文件通常作为一个项目的介绍文件,里面包含了一个项目的基本信息和作者想要展示给其他人看的介绍信息。通常来说,它并不限制格式,示例中使用的是md格式,只是因为方便书写,它也可以是README.txt,README.pdf,README.doc,它可以是任何一切人类可以阅读的文本格式,这只是一种约定俗成的规范,而非强制要求,如果你乐意,也可以不创建README文件。
这时候再执行git status命令查看仓库目前的状态,git会告诉你,这两个文件没有被追踪(untracked),如果你想要管理这两个文件,就需要显式的使用命令来进行追踪。
$ git status
On branch master
No commits yet
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
README.md
hello.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
提示中也告诉了你应该使用 git add命令来追踪这些文件,如下
$ git add hello.txt README.md
追踪文件后,再次执行git status命令,git就会告诉你这两个文件处于暂存状态(staged),即被添加到了暂存区
$ git status
On branch master
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: README.md
new file: hello.txt
在git仓库中,只有被追踪的文件才会纳入版本控制。在追踪了两个文件后,接下来修改hello.txt的文件内容
$ echo "tracked two file in repo" >> hello.txt
然后再次执行git status命令,查看仓库状态,git会告诉你,发现之前追踪的hello.txt文件已经被修改了,且新的修改没有暂存。
$ git status
On branch master
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: README.md
new file: hello.txt
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: hello.txt
此时,暂存区的状态还停留在上一次add操作时,而工作区已经有了新的修改,所以要再次执行git add来更新暂存区。
$ git add hello.txt
$ git status
On branch master
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: README.md
new file: hello.txt
查看修改
在对工作区文件做出修改过后,git status只能知晓文件的状态变化,而无法得知具体的变化细节。使用git diff命令可以解决此问题,不带任何参数执行该命令的话,它会展示工作区文件与暂存区文件的区别。比如先修改hello.txt,再执行git diff,输出如下
$ echo "update something" >> hello.txt
$ git diff
diff --git a/hello.txt b/hello.txt
index ea1ee84..5136d34 100644
--- a/hello.txt
+++ b/hello.txt
@@ -4,3 +4,4 @@ track two file in repo
12
123
123
+update something
其中a,b,分别指工作区和暂存区,@@ -4,3 +4,4 @@指的是变化位置,最后一行带有+号,表示这是新增的。加上--staged参数就会比较暂存区与上一次提交时的变化。接下来先添加到暂存区,然后再查看差异
$ git add hello.txt
$ git diff --staged
diff --git a/hello.txt b/hello.txt
index 5136d34..24fc984 100644
--- a/hello.txt
+++ b/hello.txt
@@ -5,3 +5,4 @@ track two file in repo
123
123
+update hello.txt
这一次输出的就是最后一次提交的文件和暂存区的文件的差异。
忽略文件
对于一些文件,我们并不希望将其纳入git版本控制当中,也不需要git去追踪它们的变化,比如编译好的二进制文件,程序生成的错误日志等,为此git提供了一个配置文件.gitignore,来告诉git要忽略哪些文件。下面看一个例子,这是文档站仓库的.gitignore文件:
# idea project file
.idea/
node_modules/
src/.vuepress/.cache/
src/.vuepress/.temp/
src/.vuepress/dist/
其中.idea/是忽略IntellJ IDE自动生成的项目配置文件,node_modules/是忽略掉一系列本地依赖文件,其他的要么就是忽略缓存,要么就算忽略打包文件。可以使用#来进行注释,描述忽略文件的具体信息。
文件 .gitignore 的格式规范如下:
- 所有空行或者以
#开头的行都会被 Git 忽略。 - 可以使用标准的 glob 模式匹配,它会递归地应用在整个工作区中。
- 匹配模式可以以(
/)开头防止递归。 - 匹配模式可以以(
/)结尾指定目录。 - 要忽略指定模式以外的文件或目录,可以在模式前加上叹号(
!)取反。
glob模式指的是简化过后的正则表达式,熟悉正则表达式看这个应该相当容易,下面看一些例子
# 忽略所有的go源文件
*.go
# 但不忽略main.go文件
!main.go
# 仅忽略当前目录下的go文件
/*.go
# 忽略任意目录下的src目录
src/
# 忽略当前目录下的src目录
/src/
# 忽略任意src目录下的main.go文件
src/main.go
# 忽略任意src目录下其子目录下的所有main.go文件
src/**/main.go
# 忽略当前src目录下及其子目录下所有的main.go文件
/src/**/main.go
基本上每一个语言都会有一套属于自己的.gitignore模板,比如说c++模板
# Prerequisites
*.d
# Compiled Object files
*.slo
*.lo
*.o
*.obj
# Precompiled Headers
*.gch
*.pch
# Compiled Dynamic libraries
*.so
*.dylib
*.dll
# Fortran module files
*.mod
*.smod
# Compiled Static libraries
*.lai
*.la
*.a
*.lib
# Executables
*.exe
*.out
*.app
Github有专门收集这类模板的仓库,前往github/gitignore: A collection of useful .gitignore templates了解更多。
提交修改
在将所有修改到添加到暂存区过后,就可以将暂存的文件提交到当前分支,使用git commit命令进行提交操作
$ git commit -m "initial commit"
git要求你在进行提交时,必须附带提交信息,使用-m参数来指定提交信息,如果参数为空字符串的话会中断操作,倘若不携带-m参数,会自动进入vim界面要求你必须输入提交信息,否则就无法提交到当前分支。提交成功后,git输出如下信息
[master b4c2d7f] initial commit
2 insertion(+)
其中master,就是提交到的分支,b3c2d7f是git为本次提交生成的40位sha1校验和的一部分。
每当完成了一个阶段的小目标后,将变动的文件提交到仓库,git就会记录下这一次更新。只要提交到仓库里,日后就可以通过各种手段恢复,不用担心数据丢失的可能。
跳过暂存
git提供了一个可以跳过暂存的方式,即在git commit命令后加上-a参数就可以将所有修改过的文件暂存并提交到当前分支。比如先修改了hello.txt文件
$ echo "123" >> hello.txt
然后再创建一个新文件bye.txt
$ echo "bye" > bye.txt
此时执行git status,查看仓库状态
$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: hello.txt
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
bye.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
使用git commit -a跳过暂存
$ git commit -a -m "skip stage"
再次执行git status会发现,bye.txt并没有被提交,也没有被暂存,所以跳过暂存的前提是文件首先需要被追踪,这样git才能感知到它的变化。
$ git status
On branch master
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
bye.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
历史提交
在进行一段时间的工作后,你可能会想看看以前干了些什么,可以使用git log命令查看当前仓库的提交历史。
$ git log
commit 7514cce18c477694193e61849162ad8750f873cb (HEAD -> master)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sun Sep 3 15:11:19 2023 +0800
update hello.txt
commit e538986402fb6b787a1a5778439d8bd01f316be0
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sat Sep 2 20:51:00 2023 +0800
skip stage
commit b4c2d7faf91cc2286813e7635bdad025166e08ed
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sat Sep 2 20:35:14 2023 +0800
3rd commit
commit 5ca7961d8757700652e66dec94faf9938192eccf
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sat Sep 2 16:54:09 2023 +0800
hello
commit eff484ad548c2fb78a821793898dbafa0ef8ddc9
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sat Sep 2 16:45:37 2023 +0800
initial commit
通过输出,我们可以很轻易的得知每一个提交的日期时间,作者,提交描述信息,以及sha1校验和。通过添加-p参数可以得知每一次提交的修改
$ git log -p
commit 7514cce18c477694193e61849162ad8750f873cb (HEAD -> master)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sun Sep 3 15:11:19 2023 +0800
update hello.txt
diff --git a/hello.txt b/hello.txt
index ea1ee84..5136d34 100644
--- a/hello.txt
+++ b/hello.txt
@@ -4,3 +4,4 @@ track two file in repo
12
123
123
+update something
commit e538986402fb6b787a1a5778439d8bd01f316be0
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sat Sep 2 20:51:00 2023 +0800
skip stage
diff --git a/hello.txt b/hello.txt
index 5b1f3e2..ea1ee84 100644
--- a/hello.txt
+++ b/hello.txt
@@ -3,3 +3,4 @@ track two file in repo
123
12
123
+123
...
...
...
当历史过多时可以指定显示多少条,来获得更好的查看效果
$ git log -p -1
commit 7514cce18c477694193e61849162ad8750f873cb (HEAD -> master)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sun Sep 3 15:11:19 2023 +0800
update hello.txt
diff --git a/hello.txt b/hello.txt
index ea1ee84..5136d34 100644
--- a/hello.txt
+++ b/hello.txt
@@ -4,3 +4,4 @@ track two file in repo
12
123
123
+update something
或者以图表的形式来展示提交历史,为了更有效果,拿文档站的提交历史作例子,可以看到多了一条线,这其实是其它分支合并的结果。
$ git log --graph -5
* commit 0b148b2dc402515a2c572e3464a5ec2fafcb8693 (HEAD -> main, origin/main)
|\ Merge: d8cc259 4f5d32c
| | Author: hanjiang <42080442+246859@users.noreply.github.com>
| | Date: Sun Sep 3 10:41:51 2023 +0800
| |
| | Merge pull request #9 from Axchgit/patch-1
| |
| | Update 60.slice.md
| |
| * commit 4f5d32c1a04884712d9edcbae1729c3542d63aaa
|/ Author: Axchgit <48643885+Axchgit@users.noreply.github.com>
| Date: Sat Sep 2 17:08:59 2023 +0800
|
| Update 60.slice.md
|
* commit d8cc259bccefae542af581ad329b963ec553238d
| Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
| Date: Tue Aug 29 21:58:21 2023 +0800
|
| feat(basic): 更新go1.21的一些内置函数
|
* commit 17500e16a4d1fa784ae9715e8a8c43973c494580
| Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
| Date: Tue Aug 29 21:29:32 2023 +0800
|
| feat(microservice): 更新微服务相关文章
|
除此之外,通过添加--pretty参数还可以美化git log的输出,比如每一个提交只显示一行
$ git log --pretty=oneline -5
7514cce18c477694193e61849162ad8750f873cb (HEAD -> master) update hello.txt
e538986402fb6b787a1a5778439d8bd01f316be0 skip stage
b4c2d7faf91cc2286813e7635bdad025166e08ed 3rd commit
5ca7961d8757700652e66dec94faf9938192eccf hello
eff484ad548c2fb78a821793898dbafa0ef8ddc9 initial commit
甚至支持自定义格式化,比如
$ git log --pretty=format:"%h %an <%ae> %ad %s"
7514cce 246859 <2633565580@qq.com> Sun Sep 3 15:11:19 2023 +0800 update hello.txt
e538986 246859 <2633565580@qq.com> Sat Sep 2 20:51:00 2023 +0800 skip stage
b4c2d7f 246859 <2633565580@qq.com> Sat Sep 2 20:35:14 2023 +0800 3rd commit
5ca7961 246859 <2633565580@qq.com> Sat Sep 2 16:54:09 2023 +0800 hello
eff484a 246859 <2633565580@qq.com> Sat Sep 2 16:45:37 2023 +0800 initial commit
下面是一些常用的格式化选项。
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
%H | 提交的完整哈希值 |
%h | 提交的简写哈希值 |
%T | 树的完整哈希值 |
%t | 树的简写哈希值 |
%P | 父提交的完整哈希值 |
%p | 父提交的简写哈希值 |
%an | 作者名字 |
%ae | 作者的电子邮件地址 |
%ad | 作者修订日期(可以用 --date=选项 来定制格式) |
%ar | 作者修订日期,按多久以前的方式显示 |
%cn | 提交者的名字 |
%ce | 提交者的电子邮件地址 |
%cd | 提交日期 |
%cr | 提交日期(距今多长时间) |
%s | 提交说明 |
还可以查看指定时间段的提交历史
$ git log --since="2023-09-01" --before="2023-10-01" -2
commit 7514cce18c477694193e61849162ad8750f873cb (HEAD -> master)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sun Sep 3 15:11:19 2023 +0800
update hello.txt
commit e538986402fb6b787a1a5778439d8bd01f316be0
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sat Sep 2 20:51:00 2023 +0800
skip stage
下面是一些常用的输出限制参数
| 选项 | 说明 |
|---|---|
-<n> | 仅显示最近的 n 条提交。 |
-glob=<pattern> | 显示模式匹配的提交 |
-tags[=<pattern>] | 显示匹配tag的提交 |
-skip=<n> | 跳过n次提交 |
-merges | 仅显示合并提交 |
-no-merges | 不显示合并提交 |
--since, --after | 仅显示指定时间之后的提交。 |
--until, --before | 仅显示指定时间之前的提交。 |
--author | 仅显示作者匹配指定字符串的提交。 |
--committer | 仅显示提交者匹配指定字符串的提交。 |
--grep | 仅显示提交说明中包含指定字符串的提交。 |
-S | 仅显示添加或删除内容匹配指定字符串的提交。 |
如果想要了解更多,可以使用git help log命令查看更多的细节。
检出提交
在查看完历史提交后,你可以获取一个具体的提交的sha1校验和,通过它配合git checkout命令,可以将当前工作区的状态变为指定提交的状态。例如
$ git log -2
commit f5602b9057b6219ee65cac7e9af815f9c13339df (HEAD -> master, tag: v1.0.3, tag: v1.0.1, tag: v1.0.0)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Mon Sep 4 11:13:11 2023 +0800
Revert "revert example"
This reverts commit 9d3a0a371740bc2e53fb2ca8bb26c813016ab870.
revert example
commit 9d3a0a371740bc2e53fb2ca8bb26c813016ab870
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Mon Sep 4 11:12:18 2023 +0800
revert example
$ git checkout 9d3a0a371740bc2e53fb2ca8bb26c813016ab870
Note: switching to '9d3a0a371740bc2e53fb2ca8bb26c813016ab870'.
You are in 'detached HEAD' state. You can look around, make experimental
changes and commit them, and you can discard any commits you make in this
state without impacting any branches by switching back to a branch.
If you want to create a new branch to retain commits you create, you may
do so (now or later) by using -c with the switch command. Example:
git switch -c <new-branch-name>
Or undo this operation with:
git switch -
Turn off this advice by setting config variable advice.detachedHead to false
HEAD is now at 9d3a0a3 revert example
此时工作区的文件内容已经变成了特定提交9d3a0a371740bc2e53fb2ca8bb26c813016ab870的状态,在与HEAD指针分离的情况下,所作的任何修改和提交都不会保存,除非新建一个分支。在已检出的情况下,使用如下命令来新建分支
$ git switch -c <branch-name>
也可以在一开始就新建分支
$ git checkout -b <branch-name> <sha1>
如果想要回到HEAD指针,使命如下命令即可
$ git switch -
删除文件
如果想要删除仓库中的一个文件,仅仅只是删除工作区的文件是不够的,比如新建一个bye.txt,将其添加到工作区后,再将其从工作区删除,此时执行git status会有如下输出
$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
new file: bye.txt
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
deleted: bye.txt
git知晓此变化,但是删除文件这一修改并没有添加到暂存区,下一次提交时,该文件依旧会被提交到仓库中。所以应该同时将其暂存区的文件删除,为此git提供了git rm命令来删除暂存区的文件。
$ git rm bye.txt
rm 'bye.txt'
$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
此时会发现git不再追踪此文件。需要注意的是git rm 在执行时也会删除工作区的文件,倘若仅仅只是想删除暂存区或者仓库中的文件,可以使用如下命令
$ git rm --cached bye.txt
如此一来,就不会对工作区的文件造成任何影响,将修改提交后,暂存区和仓库中的文件就会被删除,而工作区没有变化。
移动文件
当想要移动文件或重命名文件时,可以使用git mv命令来进行操作。例如将hello.txt,改为hello.md
$ git mv hello.txt hello.md
$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
renamed: hello.txt -> hello.md
git会感知到此变化,其实该操作等于执行了以下三个命令
$ mv hello.txt hello.md
$ git rm hello.txt
$ git add hello.md
就算逐条执行这三条命令,git依旧会感知到这是一次renamed操作,更多时候还是使用git mv会方便些。
简短输出
我们经常使用git status来查看本地仓库的状态,可以添加参数-s来获得更加简短的输出,git会以一种表格的方式来描述文件状态,例如
$ git status -s
A README.md
A hello.txt
上述简短输出中,左边的状态表述栏有两列,第一列表示暂存区的状态,第二列表示工作区的状态,右边则是对应的文件。A表示新追踪的文件被添加到暂存区,M表示文件被修改,D表示文件被删除,R表示文件被重命名,??表示文件未追踪,下面看一些例子。
A hello.txt // 这是一个新追踪的文件,已经被添加到暂存区,且工作区没有任何新的变动
AM hello.txt // 这是一个新追踪的文件且已被添加到暂存区,但是现在工作区有新的修改。
M hello.txt // 这是一个已被追踪的文件,工作区文件现在有了新的修改,但新修改没有被提交到暂存区
M hello.txt // 这是一个已被追踪的文件,工作区文件之前的修改已经被添加到暂存区,目前没有任何新的变动
MM hello.txt // 这是一个已被追踪的文件,工作区文件之前的修改已经被添加到暂存区后,又有了新的修改
D hello.txt // 该文件在工作区中已被删除
D hello.txt // 该文件在暂存区中已被删除
R hello.txt // 该文件已被重命名,且修改被添加到暂存区
?? hello.txt // 这是一个未被追踪的文件
当然除此之外可能还会有其他的组合,只需要知晓其意思即可。
撤销操作
在使用git的过程中,经常可能会出现一些操作失误,想要反悔的情况,git当然也给了我们反悔的机会,从不至于将仓库弄的一团糟,下面会介绍几个情况。不过需要注意的是,有些撤销操作是不可逆的。
修正提交
当你写完自己的代码后,信心满满的提交后,发现自己遗漏了几个文件,又或是提交信息中有错别字。发生这种情况时,只能是再提交一次,然后描述信息为:“遗漏了几个文件”或者是“修复了提交信息的错别字”,这样看着太别扭了,试想一下你的提交历史中都是这种东西,将会相当的丑陋。为此git commit命令提供了--amend参数,来允许你修正上一次提交。看下面的一个例子
# 第一次提交,发现搞忘了一个文件
$ git commit -m "add new file"
# 将其添加到暂存区
$ git add newfile.txt
# 然后修正上一次提交
$ git commit --amend
第二个例子
# 把main.go错写成了mian.go
$ git commit -m "update mian.go"
# 修正描述信息
$ git commit --amend -m "update main.go"
携带该参数后,git会将暂存区内的文件提交,如果说没有任何文件修改,git仅仅只会更新提交信息,修正后,提交历史中只会留下被修正的那个。
撤销提交
当你发现提交错文件了,想要撤销提交,可以使用git reset,需要注意的是git reset命令使用不当是相当危险的,因为它会丢弃指定提交后的所有修改。对于撤销级别,有三个参数可以使用
--soft:仅撤销仓库中的内容,不影响暂存区和工作区,指定撤销节点的所有修改都会回到暂存区中。--mixed:默认,撤销仓库和暂存区中的修改,但是不影响工作区。--hard:使用该参数相当的危险,因为它同时会撤销工作区的代码,携带该参数执行后,会清空暂存区,并将工作区都恢复成指定撤销提交之前的状态。
如果想要撤销多次提交,可以使用git reset HEAD^n,HEAD是一个指针,它永远指向当前分支的最新提交,HEAD^n即表示前n个提交。倘若想要撤销一个指定的提交,可以将该提交的sha1检验和作为参数使用来指定。比如下面这个命令:
$ git reset 10e5e5e7d6c7fbfa049ee6ecd0a1ee443ca1d70c
使用git reset --hard可以达到将代码回退到某一个版本的效果,不过此前工作区中的所有改动都会消失。下面会将用几个例子做演示,首先对仓库进行一次新的提交
$ echo "reset example" >> hello.txt
$ git commit -a -m "reset example"
[master c231e1f] reset example
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
$ git log -1
commit c231e1f147b07b8ed0d3c3fe58eddba736a5eab5 (HEAD -> master)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Mon Sep 4 10:06:18 2023 +0800
reset example
下面演示三个参数分别会造成什么影响,首先使用默认不带参数,可以看到此时回到了修改未暂存的状态。
$ git reset HEAD^
$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: hello.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
然后使用--soft参数,再次查看仓库状态,可以看到回到了暂存区修改未提交的状态
$ git reset --soft HEAD^
$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: hello.txt
最后使用--hard参数,此时查看仓库状态会发现什么都不会提示,因为该操作直接将工作区重置到了该次提交时的状态。
$ git reset --hard HEAD^
HEAD is now at 25cdeea a
$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
在上面的操作中,可以看到有些操作是无法恢复且相当危险的,使用git reset撤销的提交,在提交历史中会消失,如果想要找回可以使用命令git reflog,不过这是有时效性的,时间久了git会删除。
$ git reflog show
25cdeea (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{0}: reset: moving to HEAD^
7a7d12b HEAD@{1}: commit: reset example
25cdeea (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{2}: reset: moving to HEAD^
4f8190f HEAD@{3}: commit: reset example
25cdeea (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{4}: reset: moving to HEAD^
c231e1f HEAD@{5}: commit: reset example
25cdeea (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{6}: commit: a
10e5e5e HEAD@{7}: reset: moving to HEAD^
b34d4da HEAD@{8}: commit: commit1
10e5e5e HEAD@{9}: commit: commit
c7bdcd8 HEAD@{10}: commit (amend): update aaa.txt
7514cce HEAD@{11}: commit: update hello.txt
e538986 HEAD@{12}: commit: skip stage
b4c2d7f HEAD@{13}: commit: 3rd commit
5ca7961 HEAD@{14}: commit: hello
eff484a HEAD@{15}: commit (initial): initial commit
在这里我们可以看到被撤销的提交,以及其他被reflog记录的操作,想要恢复这些提交使用git reset commit-id即可。
使用git reset是比较危险的,为此,git提供了一种更加安全的撤销方式git revert。它会抵消掉上一次提交导致的所有变化,且不会改变提交历史,而且会产生一个新的提交。同样的,先做一个新提交,在使用revert。
$ echo "revert example" >> hello.txt
$ git commit -a -m "revert example"
[master 9d3a0a3] revert example
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
$ git revert HEAD
[master f5602b9] Revert "revert example"
1 file changed, 1 deletion(-)
$ cat hello.txt
hello world
track two file in repo
123
12
123
123
update something
update hello.txt
123
123
$ git log -2
commit f5602b9057b6219ee65cac7e9af815f9c13339df (HEAD -> master)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Mon Sep 4 11:13:11 2023 +0800
Revert "revert example"
This reverts commit 9d3a0a371740bc2e53fb2ca8bb26c813016ab870.
revert example
commit 9d3a0a371740bc2e53fb2ca8bb26c813016ab870
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Mon Sep 4 11:12:18 2023 +0800
revert example
$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
可以看到,在revert后,原本提交修改的内容消失了,提交历史中之前的提交仍然存在,并且还多了一个新提交。实际上git是将工作区和暂存区的内容恢复到了指定提交之前,并且自动add和commit,如果不想自动提交可以加上-n参数,此时查看仓库状态就会有提示
$ git status
On branch master
You are currently reverting commit f5602b9.
(all conflicts fixed: run "git revert --continue")
(use "git revert --skip" to skip this patch)
(use "git revert --abort" to cancel the revert operation)
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: hello.txt
git已经提示了你使用git revert --abort来删除此次revert操作,或者git revert --skip 来忽略修改。如果想要revert多个提交,则必须依次指定。例如
$ git revert [last one] [second to last]
撤销暂存
取消暂存有两种情况,一种是将新文件移出暂存区,一种是撤销添加到暂存区的修改。在先前的例子中,将新文件添加到暂存区后,查看仓库状态时,git会这样输出
$ git status
On branch master
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: README.md
new file: hello.txt
其中有这么一句:(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage),git已经告诉你了如何将这些文件取消暂存,对hello.txt执行
$ git rm --cached hello.txt
就可以将该文件移出暂存区。还有一种情况就是已经在暂存区的文件,将新的修改添加到暂存区过后,想要从暂存区撤回该修改,如下面的例子。
$ echo "123" >> hello.txt
$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: hello.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
$ git add hello.txt
$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: hello.txt
此时git已经提示了我们,使用git restore --staged来撤销暂存区的这一次修改。
$ git restore --staged hello.txt
$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: hello.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
撤销后,会发现又回到了修改未被暂存的状态了,除了使用git restore之外,还可以使用 git reset HEAD <file>来撤销暂存区的修改,后者将暂存区指定文件的状态恢复成仓库分支中的状态。需要注意的是,这些命令都是对暂存区进行操作,不会影响到仓库和工作区。
撤销修改
前面讲的都是对提交和暂存的撤销操作,当想要撤销工作区文件的修改时,将其还原成上一次提交或某一次提交的状态,在上面撤销暂存的例子中,git已经告诉我们了。
$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: hello.txt
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")
有这么一句:(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory),告诉我们,使用git restore <file>来丢弃工作区指定文件的修改。
$ git restore hello.txt
$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
执行后会发现,文件回到了修改之前,git也不再提示文件有未暂存的修改 ,使用命令git checkout -- hello.txt具有同样的效果。需要注意的是,当你对工作区修改撤销后,是无法恢复的,你最好明白你在做什么。
注意
在git中,只要是提交到了仓库中的修改,绝大多数情况都是可以恢复的,甚至被删除的分支和使用--amend覆盖的提交也可以恢复。但是,任何未提交的修改,丢弃以后就可能再也找不到了。
标签操作
在git中,你可以为某一个提交标注一个标签,表示这是一个阶段性变化,比如一个新的发行版,等等。通过命令git tag -l来查看一个仓库中的所有tag
$ git tag -l
同时它也支持模式匹配,比如
$ git tag -l "v1.*"
这行命令表示只查看主版本为1的tag。在git中,标签分为两种类型,轻量标签(lightweight)和附注标签(annotated),这两种类型还是有很大差别的,轻量标签只是一个特定提交的引用,而附注标签是存储在git中的一个完整对象,包含了许多有用的信息。
提示
人们对软件版本号的定义方式各有千秋,一个主流的方式是使用语义化版本号,前往语义化版本 2.0.0 | Semantic Versioning (semver.org)查看。
轻量标签
创建轻量标签只需要提供标签名即可,如下
$ git tag v1.0.0
在创建过后,使用git show <tagname>来查看该tag的信息
$ git show v1.0.0
commit f5602b9057b6219ee65cac7e9af815f9c13339df (HEAD -> master, tag: v1.0.0)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Mon Sep 4 11:13:11 2023 +0800
Revert "revert example"
This reverts commit 9d3a0a371740bc2e53fb2ca8bb26c813016ab870.
revert example
diff --git a/hello.txt b/hello.txt
index 1ab193a..a28df9c 100644
--- a/hello.txt
+++ b/hello.txt
@@ -8,4 +8,3 @@ update something
update hello.txt
123
123
-revert example
可以看到轻量标签显示的是commit的信息,之所以叫轻量是因为它仅仅是对提交的引用,当你仅仅只是临时需要一个tag,不想要其他的信息就可以使用轻量标签。
附注标签
创建附注标签需要用到两个额外的参数,-a参数表示创建一个annotated tags,它接收一个tag名,-m参数表示对tag的描述信息。如下
$ git tag -a v1.0.1 -m "this is a annotated tag"
创建后,对该tag执行git show
$ git show v1.0.1
tag v1.0.1
Tagger: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Thu Sep 7 14:15:28 2023 +0800
this is a annotated tag
commit f5602b9057b6219ee65cac7e9af815f9c13339df (HEAD -> master, tag: v1.0.1, tag: v1.0.0)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Mon Sep 4 11:13:11 2023 +0800
Revert "revert example"
This reverts commit 9d3a0a371740bc2e53fb2ca8bb26c813016ab870.
revert example
diff --git a/hello.txt b/hello.txt
index 1ab193a..a28df9c 100644
--- a/hello.txt
+++ b/hello.txt
@@ -8,4 +8,3 @@ update something
update hello.txt
123
123
-revert example
会发现除了展示commit的信息之外,还会展示标记标签的人,日期,信息等。
指定提交
git tag命令在创建标签时,默认是为HEAD指针,也就是最新的提交创建tag,当然也可以是一个特定的提交。只需要将该提交的sha1校验和作为参数即可。如下
$ git tag -a v1.0.2 -m "specified commit tag" eff484ad548c2fb78a821793898dbafa0ef8ddc9
创建完后,查看tag信息
$ git show v1.0.2
tag v1.0.2
Tagger: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Thu Sep 7 14:23:57 2023 +0800
specified commit tag
commit eff484ad548c2fb78a821793898dbafa0ef8ddc9 (tag: v1.0.2)
Author: 246859 <2633565580@qq.com>
Date: Sat Sep 2 16:45:37 2023 +0800
initial commit
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..933885d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/README.md
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
+#Hi there
diff --git a/hello.txt b/hello.txt
new file mode 100644
index 0000000..ddfb619
--- /dev/null
+++ b/hello.txt
@@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
+hello world
+track two file in repo
这样,就可以为一个指定的提交创建tag了。
删除标签
在本地仓库删除一个tag,可以使用命令git tag -d <tagname>,比如
$ git tag -d v1.0.2
Deleted tag 'v1.0.2' (was 13948de)
删除后,再查看tag就会发现没有了
$ git tag -l
v1.0.0
v1.0.1
不过需要注意的是,这仅仅只是在本地仓库删除标签,如果有远程仓库的话,需要单独删除,可以使用如下命令
$ git push origin --delete <tagname>
推送标签
当你的本地仓库关联了一个远程仓库后,如果你本地创建了tag,再将代码推送到远程仓库上,远程仓库是不会创建tag的。如果你想要推送某一个指定的标签可以使用如下命令
$ git push <remote> <tagname>
例如
$ git push origin v1.0.3
Enumerating objects: 1, done.
Counting objects: 100% (1/1), done.
Writing objects: 100% (1/1), 151 bytes | 151.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 1 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
To https://github.com/246859/git-example.git
* [new tag] v1.0.3 -> v1.0.3
如果你想要推送所有标签,直接加上--tags参数即可。
$ git push origin --tags
Enumerating objects: 27, done.
Counting objects: 100% (27/27), done.
Delta compression using up to 16 threads
Compressing objects: 100% (23/23), done.
Writing objects: 100% (27/27), 2.32 KiB | 790.00 KiB/s, done.
Total 27 (delta 5), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0
remote: Resolving deltas: 100% (5/5), done.
To https://github.com/246859/git-example.git
* [new tag] v1.0.0 -> v1.0.0
* [new tag] v1.0.1 -> v1.0.1
这样一来,远程仓库上的tag就与本地仓库同步了。
检出标签
使用命令git checkout <tagname>,就可以将工作区的内容变为该标签所提交时的状态,如
$ git checkout v1.0.3
Note: switching to 'v1.0.3'.
You are in 'detached HEAD' state. You can look around, make experimental
changes and commit them, and you can discard any commits you make in this
state without impacting any branches by switching back to a branch.
If you want to create a new branch to retain commits you create, you may
do so (now or later) by using -c with the switch command. Example:
git switch -c <new-branch-name>
Or undo this operation with:
git switch -
Turn off this advice by setting config variable advice.detachedHead to false
HEAD is now at f5602b9 Revert "revert example"
git提醒你,现在处于与HEAD指针分离的状态,现在你做的任何的修改和提交都不会对仓库造成任何影响。如果你想要保存这些修改,可以创建一个新的分支
git switch -c <branch-name>
或者你也可以在一开始就创建一个新的分支
$ git checkout -b <brancn-name> <tagname>
而后面如果你想要希望将这些修改同步到仓库中,这就涉及到后面分支这一文要讲的内容了。如果你想要回到头指针,执行如下命令即可。
$ git switch -
命令别名
对于你经常使用的命令,如果觉得每次都要输入完整的命令而感到厌烦,命令别名可以帮到你。例子如下
$ git config --global alias.ci commit
$ git config --global alias.st status
上述命令分别为commit和status命令创建了别名,由于添加了--global参数,所以别名可以全局使用。执行别名试试
$ git st
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean
还有三个参数要提一下,分别是
--add,表示添加别名--replace-all,表示覆盖别名--unset,表示删除别名
除此之外,也可以使用命令来清空所有别名
$ git config --global --remove-section alias
这个命令会直接将配置文件中的alias部分删掉。
配置文件
除了使用命令之外,也可以使用配置文件,也就是.gitconfig文件,windows一般是c:/$user/.gitconfig,linux一般是$HOME/.gitconfig。打开配置文件就可以看到如下内容
[alias]
st = status
ls = ls
env = echo
env = echo revert
env = !go env
外部命令
除了给git自身的命令加别名外,也可以是外部命令,在添加外部命令时,需要在命令前加上!来表示这是外部命令。格式为
$ git config --gloabl alias.<aliasname> <!externalcmd>
例如下面的命令,需要注意的是别名必须是单引号括起来。
$ git config --global alias.env '!go env'
执行别名试试,就可以看到go的环境变量。
$ git env
set GO111MODULE=on
set GOARCH=amd64
...
